Portfolio Management
Home » Portfolio Management
Get life insurance today.

Portfolio Management
What is Portfolio Management?
Portfolio management is the process of managing a portfolio of investment mix that includes Stocks, Bonds, Mutual fund, FD and RD. In general a portfolio manager is appointed to manage a portfolio and its performance.
- It primarily aims at guiding an organization or an Individual to make sound decisions
- It ensures that the risk appetite of the investor does not affect him.
- The key factors involved in portfolio management include risk, decision making and control.
- Portfolio management ensures flexibility of an individual’s and companies Portfolio.
- Portfolio management maximizes the return on investment.
Types of Portfolio Management
As the figure above illustrates, there are 4 kinds of portfolio management.
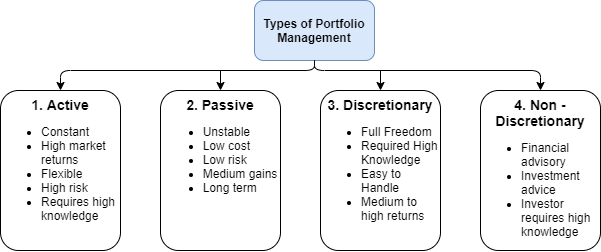
1. Active
Active portfolio management needs a greater level of market knowledge. The fund manager who aims at using an active strategy expects a market return. The active strategy requires a constant evaluation and quantitative analysis of the market. Furthermore, it requires a clear understanding of the business cycle.
- Active portfolio management ensures a greater level of market returns
- Another benefit of active portfolio management is that the fund manager has better flexibility.
- Active strategies are suitable for investors with great market knowledge and experience. It is suitable for an investor with a greater risk appetite.
2. Passive
Passive portfolio management is not concerned about beating the market because the proponent subscribe to the efficient market hypothesis
- Investors who seek to reduce risk often prefer passive portfolio management.
- Passive strategy is one of the low-cost strategies to execute.
- These strategies provide better gains in the long term.
3. Discretionary
The fund manager takes complete discretion in investment decisions for the customer. The investment manager takes all the buy and sale decision and use them to make the best out of it. This strategy can be offered by only experts who possess a great level of knowledge in this field.
- One of the biggest advantages of this type of portfolio management is that they make our lives in terms of investment decision.
- All the burden and hassle of decision making is transferred to an expert.
4. Non-discretionary
Non-discretionary portfolio management is a type of asset management. Here, the manager acts as a financial adviser for the individual. The manager states the advantages and disadvantages of the options. Finally, the individual owns the discretion.
- The merit of this type of portfolio management is that the manager gives you the choices and individuals get to choose their decisions.
Investing.com has a different approach towards categorizing portfolio management. The New Dayslightly-Trader, The Experienced Investor, The Crypto & Currency Trader. (Source)
Who is a Portfolio Manager?
A portfolio manager is a person who manages the portfolio of a person or group. Moreover, they are also responsible for the managing the portfolio on a daily basis. The portfolio management plays an active or a passive role in terms of management of portfolios. They are the people responsible for formulation of the plans and they should possess excellent research skills.
Roles of Portfolio manager
1. Investment decisions
A portfolio manager ensures that clients make the best decisions regarding their investment. For this purpose, the portfolio manager is expected to understand the client’s profile. The client profile involves knowing about the customer’s age category, income level and risk appetite. Uncertain situations arise at any point in one’s life, keeping aside a sum for investment would be the best option and that action could be carried out with the help of portfolio management. The Portfolio Manager will also provide investment advice to his clients.
2. Investment tools
The prime responsibility of the portfolio manager is to ensure that the clients are aware of the several investment tools that are available in the market. The manager should further take another step and explain the benefits and drawbacks of those tools and assess them for risk and returns.
The manager should also consider the financial position of the client while carrying out the duty. After analysis of the option, the manager should give the client the option that is suitable.
3. Customization of plan
Portfolio management requires a clear understanding of the customer’s needs and his problem. The conundrum in such a field begins with understanding the client’s dynamics. Since every client’s needs and different, it is not easy to carry out such a duty.
Thus, the portfolio manager’s key role is to understand and plan a customized strategy. This consists of factors like risk, return and market conditions. The plan should consider the financial stability and risk appetite of the customers.
4. Unbiased service and professionalism
A portfolio manager should treat all his clients equally and prioritize the needs of the clients. He should ensure that client’s needs and expectations are satisfied with his/her service. In simple words, he/she should put the satisfaction first rather than escaping the
Responsibilities.
Moreover, his relationship with the client has to be highly professional. It should ensure that the client’s financial details and information are safe and secure.
5. Decision making & communication
A portfolio manager is expected to make a quick and prompt decision. For instance, after making an investment decision the customer expects high asset performance. There is always a probability factor that is tied up with the investment performance.
Let’s consider an investment is not performing well due to market condition. Then, the manager should step in and make decisions relating to asset withdrawal and asset reinvestment. Communication is essential for the relationship that the client and the manager have. It helps to understand the perspective of the client. The manager should ensure that he updates the client about the performance of the asset.
6. Tracking performance
Tracking the performance of the asset is another vital role of the portfolio manager. After understanding the client’s status and guiding them to invest in certain assets the manager should make sure that assets are performing according to the standards.
The manager generally uses an optimization tool to evaluate the performance of the asset. In case if the assets do not perform well, it is the duty of the manager to communicate them to the client and suggest ideas for reinvestment. The Portfolio manager performs frequent portfolio analysis to track the performance of his investments.
7. Other responsibilities
The manager should explain all the financial information to the client. The client trusts the portfolio manager and hands over the money to invest. Hence, the investor should receive every update about the investment and its performance.
Moreover, the manager should ensure that the client is not neglected, due to adverse work condition. The portfolio manager shouldn’t ignore any client queries.


